- Visibility 227 Views
- Downloads 235 Downloads
- Permissions
- DOI 10.18231/j.ijpns.2022.024
-
CrossMark
- Citation
Clinical case report: Chronic kidney disease and ESKD (End stage kidney disease)
- Author Details:
-
Onaisa Aalia Mushtaq
-
Bushra Mushtaq
-
Javaid Ahmad Mir *
Abstract
Introduction: Chronic kidney disease include fibrosis, loss of renal cells and infiltration of renal tissue by monocytes and macrophages. The pathophysiology may include protein uria, hypoxia and excessive angiotensive II production. Hypoxia also contributes to disease progression. The disease has a vast number of clinical manifestations which include abnormalities in laboratory tests, hypertension, fatigue and poor appetite. There are five stages of CKD and in stage 5 the full blown clinical manifestations of end -stage renal disease are evident.
Medical this disease can be managed by:
1. Controlling blood pressure. 2. Managing blood glucose level to maintain HbA1c below 7%. 3. Managing hyperlipidemia with diet and cholesterol lowering drugs. 3. Managing and treating emerging manifestations of renal failure. 4. Prepare clients for renal replacement therapy when necessary.
Conclusion: Patients condition (general condition) was fair, GCS 15/15,but had ineffective coping strategies, he was very much worried about his condition & renal transplant. He was not satisfied about the treatment received. Doctors have planned to discharge him till they arrange a donor for kidney.
Introduction
Biographic information
Health History
|
Name: |
XXXXX |
|
Age: |
55 year |
|
Sex: |
Male |
|
Address: |
xxxxxx |
|
Religion: |
xxxxx |
|
Education: |
Nil |
|
Occupation: |
Businessman |
|
Mrd no: |
1212454 |
|
Ward: |
Nephrology |
|
Unit: |
Hemodialysis |
|
Date of admission: |
----------- |
|
Marital status: |
Married |
|
Source of information: |
Patient and health records (case sheet) |
|
Diagnosis: |
CKD- ESRD |
|
Head of the unit: |
------------ |
|
Blood Group: |
AB+ve |
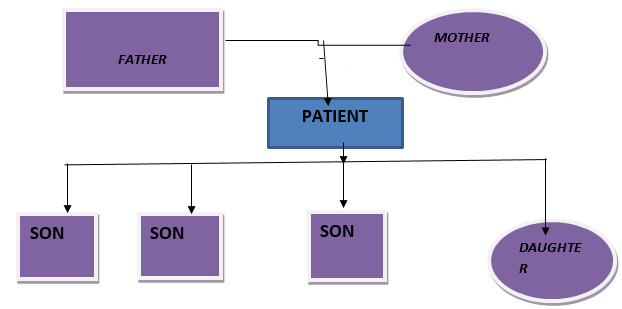
Type of family
Nuclear
Family medical history
Father of the patient is hypertensive and mother is having hypothyroidism. There is no history of diabetes or any other chronic disease within the family.
Health practices
As patient belongs to the middle class and educated family, there is no misconception or superstition related to the course of any disease. They avail health facilities to some extent.
Persoal History
Life style habits and beliefs: Ex-smoker and believes in diet control
History of any allergy: Not significant
Activity: Severe impairment in daily routine activity, fatigue on exertion
Cognition: No cognitive impairment
Rest and sleep: Decreased sleep
Self-perception: Patient is aware about his disease condition
Coping stress: Good coping strategy
Details of milestones and development
Normal mental and physical growth
Socio-economic status
Belongs to the middle class and educated family, well satisfied, happy and having good interpersonal relationship with others.
Dietary History
Both vegetarian and non-vegetarian
|
Timing |
Menu |
|
Morning |
1 cup tea + 1 bread |
|
Mid-Morning |
Nil |
|
Lunch |
Rice with vegetables(1/2 plate) inadequate amount |
|
Evening |
1 cup tea +1 bread |
|
Dinner |
Rice with vegetables (inadequate amount) |
Environmental History
Housing Pattern: Pucca house and well ventilated
Waste /Excreta disposal:Closed, use of dustbins and dumping
Drinking Water Supply: Tap water
Environmental Sanitation: Adequate
Physical examination
Mental Status: Conscious, oriented to time, place and person
Body Development: Weak
Height and Posture: 5 ft 5” Straight and erect posture
Weight: 75kgs
Hygienic condition: Fair
Vital Signs: B P 160/90mmhg, Temp 990F, Respiration 18 breaths /min, Pulse 80/min
Skin: Normal texture but looks shiny, pitting type edema on feet. Skin color is pale.
Head: Hair clean no tangles & pediculosis. Head is normal in shape no deformity noticed.
|
Eye Brows |
Symmetrical |
|
Eye Lashes |
Normal in position |
|
Eye lids |
Edematous |
|
Conjunctiva |
Pale |
|
Pupils |
Normal size reacting to light |
|
Vision |
Normal |
|
External ears: |
No discharge |
|
Alignment: |
Symmetrical |
|
Hearing Acquity: |
Normal |
|
Lips: |
Bluish (cyanosis) and dry |
|
Tongue: |
Dry |
|
Gums: |
Normal with no any bleeding and gingivitis |
|
Teeth |
No missing teeth but caries present. |
|
S.no |
Test |
Patients value |
Normal range |
Remarks |
|
1 |
CBC |
|
|
|
|
|
Hb |
6.4gm/dl |
12-14gm/dl |
Decreased |
|
|
WBC’S |
10.5 |
4.8-10.0 |
Increased |
|
|
RBC’S |
3.0*106ul |
3.5-5.2 |
Decreased |
|
|
PLATELETS |
170*103/ul |
140-440*10ul |
Normal |
|
|
MCV |
82.8 |
75.0-95.0 |
Normal |
|
|
HCT |
35.2 |
35-47 |
Normal |
|
2 |
KFT |
|
|
|
|
|
Urea |
184mg/dl |
10-20mg/dl |
Increased |
|
|
Creatinine |
15.02mg/dl |
0.5-1.5mg/dl |
Increased |
|
3 |
LFT |
|
|
|
|
|
Bilirubin |
1.8mg/dl |
0.5-1.0mg/dl |
Increased |
|
|
AST |
22U/L |
15-30U/L |
Normal |
|
|
ALT |
20U/L |
10-35U/ml |
Normal |
|
|
ALP |
80U/L |
50-120U/L |
Normal |
|
|
Protein |
4.2mg/dl |
6-8gm/dl |
Decreased |
|
|
Albumin |
2.7mg/dl |
4.5-5.5gm/dl |
Decreased |
|
|
Blood Sugar |
97mg/dl |
|
|
|
4 |
Electrolytes |
|
|
|
|
|
PH |
7.35 |
7.35-7.45 |
Normal |
|
|
Na |
139meq/l |
135-145meq/l |
Normal |
|
|
K |
9.23meq/l |
3.5-4.5meq/l |
Increased |
|
|
HCO3 |
20 |
|
|
|
|
PO2 |
90% |
90-100% |
Normal |
|
|
PCO2 |
40 |
35-45 |
Normal |
|
5 |
Urine Analysis |
|
|
|
|
|
Color |
Yellowish |
|
|
|
|
Albumin |
Traces |
|
|
|
|
Sugar |
Nil |
|
|
|
|
Pus cells |
12-18 |
|
|
|
|
Erythrocytes |
24-30 |
|
|
|
|
Ca oxalates |
A few |
|
|
|
7 |
Serology |
|
|
|
|
|
HbSAg |
Non-Reactive |
|
|
|
|
HCV |
Non-Reactive |
|
|
|
|
HIV |
Non-Reactive |
|
|
|
Stages |
Description |
GFR: ml/min/1.73m2 |
|
1 |
Slight kidney damage with normal or increased filtration. |
_> 90 |
|
2 |
Mild decrease in kidney function |
60-89 |
|
3 |
Moderate decrease |
30-59 |
|
4 |
Severe decrease |
15-29 |
|
5 |
Kidney failure |
Less than 15 |
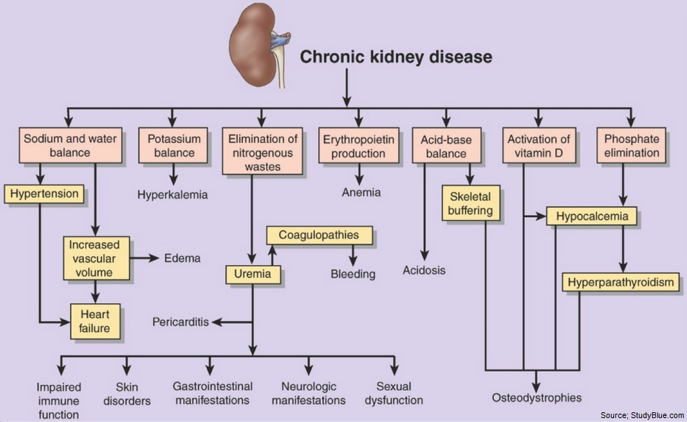
Signs & symptoms
|
According to Book |
According to Patient |
|
Weakness and fatigue |
Present |
|
Inability to concentrate |
Present |
|
Confusion |
Absent |
|
Restlessness or weakness of legs |
Present |
|
Seizures |
Absent |
|
Behavioral changes |
Present |
|
Burning feet(sole of feet) |
Absent |
|
According to book |
According to patient |
|
Dry,flaky and shiny skin |
Present |
|
Thin & brittle nails |
Absent |
|
Thin hair |
Absent |
|
According to book |
According to patient |
|
Hypertension |
Present |
|
Pitting edema |
Present |
|
Periorbital edema |
Present |
|
According to book |
According to patient |
|
Tachypnea |
Present |
|
Shortness of breath/shallow breath |
Present |
|
Acetone breath smell |
Present |
|
Kussmaul type respiration |
Present |
|
According to book |
According to patient |
|
Anorexia, nausea and vomiting |
Present |
|
Metallic taste |
Absent |
|
According to book |
According to patient |
|
Anemia |
Present |
|
According to book |
According to patient |
|
Changes in urine output |
Present |
|
Infertility |
Absent |
|
Testicular Atrophy |
Absent |
|
According to book |
According to patient |
|
Muscle cramps |
Present |
|
Bone pain |
Absent |
|
Loss of muscle strength |
Present |
|
Fractures |
Absent |
|
Joint pain |
Present |
|
According to the Book |
According to patient |
|
Hyperkalemia |
Present |
|
Anemia |
Present |
|
Hypertension |
Present |
|
Pericarditis |
Absent |
|
Pericardial effusion &tamponade |
Absent |
|
Bone disease |
Absent |
|
Name of the drug |
Action |
Dosage& Route |
Indications |
Side effects |
Contraindications |
Nurses responsibility |
|
Furosemide (Lasix) |
Diuretic Inhibits the reabsorption of Na & Cl, acts on loop of Henle and DCT.Increases excretion of water,Na,Cl,K,Mg and calcium.It also decreases B.P. |
20mg or 40mg Oral/ IV |
Hypertension, Edema, Heart failure,Renal disease and hepatic impairment. |
CNS- blurred vision,headache, dizziness, vertigo. ENT-tinnitus, hearing loss. CV-hypotension. GU-excessive urination and others like fluid & electrolyte imbalance. |
Hypersensitivity Severe hypotension, hepatic coma, anuria,not indicated in alcohol intolerance. |
Asses fluid status, check B.P & pulse before giving Lasix. Notify physician if anuria occurs. Caution patient to change position slowly to minimize orthostatic hypotension. Advice the patient contact doctor immediately if weakness,cramps, nausea, dizziness occurs. |
|
Nifedipine |
Antihypertensive agent that inhibits Ca ion movement across cell Action membranes, Depressing contraction of cardiac & vascular smooth muscles. Thus decreases blood pressure. |
10mg Oral Dosage & route |
Hypertension And Indications chronic stable angina. |
Hypotension, peripheral edema, dizziness, Side effects nausea, dyspnea. |
Severe hypotension |
Administer it early in the morning. Nurses responsibility Do not crush or chew sustained release dosage forms. |
|
Pantoprazole and Domperidone |
Proton pump inhibitor and decreases the secretion of HCl. Domperidone is a dopamine-receptor blocking agent.Its action on the dopamine receptors in the chemo-emetic trigger zone produces an anti-emetic effect. |
40mg Oral |
Peptic ulcer, NSAID associated peptic ulcer.Zollingers Ellison syndrome. Gastro-esophageal reflux. |
Headache, Insomnia, confusionDiarrhea, abdominal pain. Urticariaor rash, Abdominal cramps ,coated tongue etc. |
Hypersensitivity to drug and lactation. Hypotension |
Administer it an empty stomach. Check for any side effects and inform physician whenever necessary. Check for hypotension. |
|
Predicort (prednisolone) |
Steroid |
20 mg Oral |
In immuno –compromised patients, Edema, rheumatic diseases, cancers, inflammatory conditions. |
Gastric irritation, Masculine features. |
In gastric/ peptic ulcers, Ca stomach etc. |
Should not be stopped abruptly but should be tapped and should be given not without H2 blocker. |
|
Date & time |
Temperature |
Pulse |
Respiration |
Blood Pressure in mmHg |
Summary/ Nurses Notes |
|
16/3/2021 10AM |
980F |
80/Min |
22/min |
150/90 |
General condition of the patient is fair,patientconscious.oriented& GCS 15/15.Medications given and I/O chart maintained. |
|
17/3/2021 10AM |
98.20F |
88/min |
20/min |
160/100 |
Patient’s condition stable,B.P on higher side, due drugs given and intake output chart maintained. |
|
18/3/2021 10AM |
98.60F |
90/min |
18/min |
146/100 |
Patient remained stable Hemodynamically. All vital signs are within normal range. |
|
19/3/2021 10AM |
990F |
98/min |
22/min |
160/90 |
Patient is conscious, well oriented and responding to verbal commands. Due drugs given. |
|
Assessment |
Nursing diagnosis |
Objectives |
Interventions |
Rationale |
Evaluation |
|
Subjective data: Patient says that he is having loss of appetite. |
Imbalanced nutrition less than body requirements related to anorexia, nausea& vomiting. |
Improve the nutritional status of patient. |
Assess the nutritional status of the patient; lab investigations. |
Baseline data allow for monitoring of changes and evaluating effectiveness of interventions. |
Positive improvement in nutritional status. |
|
Objective data: Patient looks very weak & is not taking enough food as he is supposed to. |
Provide food in small amounts but at frequent intervals. |
Increased dietary intake is encouraged. |
|||
|
Provide patients food preferences within dietary restrictions. |
|||||
|
Educate the patient & relatives regarding importance of food & balanced diet. |
|||||
|
Subjective data: Patient saysthat he is unable to perform ADL. Objective data: Patient looks very tired, pale, lethargic& was on dialysis. |
Activity intolerance related to fatigue, anemia and dialysis procedure. |
Enable the patient to perform his daily living activities. Provide assistance to the patient. Minimize the fatigue. |
Assess factors contributing to fatigue, fluid & electrolyte imbalance |
Indicates factors contributing to severity of fatigue i.e. fluid & electrolyte imbalance. |
Patient participated in some activities of daily living. |
|
|
Promote independence in self-care activities as tolerated. |
Promotesself-esteem. |
|||
|
Encourage alternating activity with rest. Encourage the patient to take rest after dialysis. |
Promotes relaxation& comfort Prevents undue exertion & relieves stress. |
||||
|
Assessment |
Nursing Diagosis |
Objectives
|
Interventions
|
Rationale
|
Evaluation
|
|
Subjective data: Patient complains of swelling in hands and feet. |
Excess fluid volume related to decreased urine output and retention of other waste products. |
Maintain fluid volume status within established parameters. |
1.Assess the weight, assess extremities for presence of edema. |
Assessment provides baseline & ongoing database for monitoring changes and evaluating the outcome. |
Edema lessen to some extent. |
|
Objective Data: On palpation, pitting edema is seen on feet. |
2.Monitor intake and output. |
Fluid restriction will be determined on the basis of weight, urine output and response to therapy. |
|||
|
Monitor vital signs and B.P. |
Oral hygiene reduces the dryness of oral mucus membrane. |
||||
|
4.Limit fluid intake to prescribed volume. |
Explanation promotes patients cooperation with fluid restriction. |
||||
|
5.Encourage frequent oral hygiene. |
|||||
|
6.Explain the patient & family about the importance of fluid restriction |
|
Table 19 Cont.. |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Assesment |
Nursingdiagnosis |
Objective |
Interventions |
Rationale |
Evaluation |
|
Subjective data: Patientis complaining of headache. |
Headache related to increased blood pressure(hypertension) |
Relieve the headache by diverting attention of patient. |
Assess the level of pain due to headache. |
This may help to distract the patient from disturbedthoughts. |
B.P is within normal limits. |
|
Objective data: Patient is very irritable & restless. Blood pressure is 160/90 |
2.Provide diversion therapy by engaging the patient in verbalization and for Watching TV. |
-Increased activity may aggravate pain. |
|||
|
Provide comfortable position. |
Diet & drugs have an utmost importance in controlling hypertension. |
||||
|
Encourage compliance with dietary regimen and anti-hypertensive drugs as prescribed. |
|||||
|
Inform the patient to report signs of fluid overload, vision changes,seizures. |
|||||
|
Administer drugs as prescribed. |
|||||
|
Subjective data: Patient says, “I am fed-up with this disease & dialysis”. |
Deficient knowledge regarding disease and treatment. |
Educate the patient about the disease, importance of dialysis and make him able to take care of himself. |
Provide explanation of renal function, condition of disease and treatment regime. |
An environment of mutual understanding can enhance the learning process. Participation in self-care assists the patient to gain a sense of dignity &feeling of self-worthy. |
Verbalize to make adjustments in lifestyles. |
|
Objective data: Patient has apprehensions related to CKD,HTN and Dialysis. |
Establish rapport with the patient and family and clear their all doubts related to renal transplant. |
||||
|
Verbalize plans to continue as normal life as possible and identify patients coping strategies. |
|
Nurses Action |
Patient had uncontrollable high blood pressure, So I administered diuretics as prescribed. |
Patients action is limited |
|
|
Maintained intake output chart of my patient, checked vital signs. |
|
|
Nurses Action |
Assisted patient in performing various self-care activities. |
Patient action |
|
|
Assisted him in ambulation. |
|
|
|
Checked his vital signs. |
|
|
|
Patient is able to perform self-care activities like brushing teeth. |
|
|
|
Patient shows concern regarding intake of medicines at prescribed time and is now taking the medications himself(orally). |
|
|
Nurses Action |
Educated the patient to take low sodium diet. |
Patient is taking all medication and is following the said advice. |
|
|
Educated him about the importance of balancing rest and activity periods. |
|
|
|
Elevated the head end of bed to provide comfort to patient. |
|
|
|
Advised him to take medicines on time. |
|
|
|
Advised him to be regular for dialysis and follow up checkups. |
|
Nose
External Nares: No discharge, no nasal flaring
Nostrils and septum/bridge
No discharge and no inflammation or any DNS.
Neck
Thyroid and lymph nodes: Normal, no enlargement noticed
Systemic physical examination
CNS: Patient conscious, oriented and responding to verbal commands.GCS 15/15 E4V5M6
Cardio vascular system: Pulse: Normal rate and rhythm(85b/min).1S2: ++ and no murmurb. B.P: 160/90 mmHg
Respiratory system: Respiratory rate 20b/min, B/L air entry Normal, No crepts/wheeze.
Gastrointestinal system: P/A soft, Non tender with active bowel sounds, slightly distended & having anorexia.
Genitourinary system: Oliguria. Urine is pale yellowish in color& not catheterized.
Musculoskeletal system: Normal range of motion. Absence of any congenital abnormality. Muscle cramps present. Muscle tone is strong and no muscle atrophy. Pitting edema in feet. Reflexes normal.
Motor functions: Motor function is normal and normal cranial function.
Integumentary system (skin): Normal skin texture. Skin color pale.
Sensory function: Normal sensations to temperature, pain, touch etc.
Reflexes: Biceps reflex: Normal, Triceps reflex: Normal, Patellar reflex: Normal, Achilles reflex:, Normal, Deep tendon reflex: Normal
Specific investigations
USG
Bone Marrow Aspiration
Renal Biopsy reveals chronic sclerosing disease.
Definition, cause and pathophysiology of disease (Patient)
Definition
Chronic kidney disease or chronic renal disease is a progressive loss of renal function over a period of months or years in which metabolic, fluid and electrolyte balance falls, resulting in uremiaor azotemia. In this the GFR falls below 10% of the normal.[1], [2], [3], [4], [5] All individuals with a glomerular filtration rate (GFR)<60ml/min/1.73m2for 3 months are classified as havingchronicrenal disease irrespective of the presence or absence of kidney damage. End-stage renal disease (ESRD) occurs when GFR is less than 15ml/min/m2.
Causes
Heredity
Glomerular dysfunction
Cardiovascular disease or cardiovascular risk factors such as Hypertension
Poly cystic kidney disease, Glomerular Nephritis, Urinary tract obstruction, Bladder Tumor, Urethral obstruction, Hypertensive nephrosclerosis.
Diabetic nephropathy
Multi-system disease with potential for kidney involvement
Nephrotoxic drugs
Other causes are
HIV infection
Recurrent urinary or Kidney stones (> 1 episode per year
Chronic kidney infection and certain cancers
Vasculitis
Regular use of NSAID
Vesicoureteral reflux
Multiple myeloma
Diagnostic Evaluation
History taking, physical assessment,Urine analysis, Blood chemistry, KFT, LFT, serology, ECG, USG, bone marrow aspiration.
Pathophysiology
Approximately 1 million nephrons are present in each kidney, which contributes to the total GFR. In the case of renal disease regardless of the etiology the nephron has an innate ability to maintain GFR, despite progressive destruction of nephron by hyper filtration and compensatory hypertrophy.[6], [7], [8], [9], [10]
This nephron adaptability allows for continued normal clearance of plasma solutes. Plasma levels of substances i.e. urea & creatinine starts to increase only if total GFR has decreased to 50%, when the renal reserve has been exhausted. The plasma creatinine value will approx. double with 50% reduction in GFR.
In end-stage renal failure or uremia more than 85% loss of nephron occurs, less than 10% of normal GFR, BUN& serum creatinine at high levels. Anemia, azotemia, metabolic acidosis & urine-specific gravity are fixed at 1.010 oliguria & symptoms of renal failure appears. It is at this Stage where most of the patient face much difficulty in carrying out basic activities of daily living because of the cumulative effect and extent of the symptoms.
Medical Management
Pharmacological theraphy
Tab Lasix 40 mg OD
Tab Nifedipine 10mg BD
Tab Pantop D 40 mg BD
Tab Predicort 20mg BD
Nursing diagnosis
Impaired nutritional status less than body requirements related to anorexia, nausea & vomiting.
Activity intolerance related to fatigue, anemia and dialysis.
Excess fluid volume related to decreased urine output and retention of other waste products.
Headache related to increased B.P(hypertension).
Deficient knowledge regarding disease and treatment.
Application of Nursig Theory
I have selected Orem’s Nursing System theory for application of nursing process on my patient with CKD-ESRD. The focus of Orem’s theory is to enhance patient’s ability for self-care. Three systems exist within this model: The Wholly Compensatory in which the nurse provides the total care; The Partially Compensatory in which the patient and nurse share responsibility of care; Supportive educative system in which patient has the primary responsibility for personal health, with the nurse acting as a consultant.
Discharge teachings/health education
Advised him to Limit the intake of protein rich foods such as kidney, brains, meat extracts etc.
Advised him to take Low potassium diet & Low salt is also encouraged.
Educated to adopt the treatment regimen.
Advised him to get plenty of rest and get more sleep at night.
Advised him to move around and bend his legs to avoid getting blood clots due to rest for a long period of time.
Advised him to keep record of hi daily weights.
Instructed to report hospital if any complication arises.
Advised for regular checkup of BP and blood sugar.
Advised the patient for maintenance hemodialysis.
Assisted him to develop effective coping in day to day life.
Educated regarding renal transplant and its misconceptions.
Instructed the patient to maintain hygiene.
Advised for regular follow up services.
Adherence to dietary restrictions and prescribed medications.
Conclusion
Patients condition (general condition) was fair, GCS 15/15,but had ineffective coping strategies,he was very much worried about his condition & renal transplant. He was not satisfied about the treatment received. Doctors have planned to discharge him till they arrange a donor for kidney.
During case study, health education was provided to patient, checked his vital signs. Monitored blood pressure at regular intervals. Maintained intake output chart. Administered medications as prescribed. Educated the patient and his family regarding maintenance hemodialysis. Advised the patient to come for regular follow- up.
Source of Funding
None.
Conflict of Interest
None.
References
- Brunner S. Medical Surgical Nursing.. . 2010;2:1325-33. [Google Scholar]
- Murgesh N. A concise Textbook of Pharmacology. . 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Mir J, Bushra. Clinical Case Report on Bipolar Affective Disorder. J Paediatr Nurs Sci. 2022;8(1):10-4. [Google Scholar]
- Mir J, Mushtaq B, Mushtaq OA. Mental illness vs mental retardation. Int J Med Paediatr Oncol. 2022;8(1):10-4. [Google Scholar]
- Mushtaq B. Process Recording, a way of Therapeutic Communication Between a Nurse and Client with Psychiatric Illness. J Counselling Fam Thera. 2020;1(1):1-4. [Google Scholar]
- Mir J, Mushtaq B. Crisis as psychiatric emergency and Role of psychiatric nurse.. JONA J Nurs Administration. 2018;1(2). [Google Scholar]
- Mushtaq B, Mir JA. Psychiatric rehabilitation. MOJ Drug Design Develop Ther. 2018;2(5):214-5. [Google Scholar]
- Mushtaq B, Mir JA. Effectiveness of Online Education during Covid-19 Pandemic in Kashmir According to the Teachers. Onaisa Aalia Mushtaq. 2022;4(1):6-15. [Google Scholar]
- . Assessing national capacity for the prevention and control of noncommunicable diseases: report of the 2019 global survey. Geneva: World Health Organization. . . [Google Scholar]
- . The Report of the International Narcotics Control Board for 2019. . . [Google Scholar]
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Type of family
- Persoal History
- Dietary History
- Environmental History
- Physical examination
- Signs & symptoms
- Nose
- Nostrils and septum/bridge
- Neck
- Systemic physical examination
- Specific investigations
- Definition
- Causes
- Other causes are
- Diagnostic Evaluation
- Pathophysiology
- Medical Management
- Application of Nursig Theory
- Conclusion
- Source of Funding
- Conflict of Interest
- References
How to Cite This Article
Vancouver
Mushtaq OA, Mushtaq B, Mir JA. Clinical case report: Chronic kidney disease and ESKD (End stage kidney disease) [Internet]. J Paediatr Nurs Sci. 2022 [cited 2025 Oct 10];5(3):145-154. Available from: https://doi.org/10.18231/j.ijpns.2022.024
APA
Mushtaq, O. A., Mushtaq, B., Mir, J. A. (2022). Clinical case report: Chronic kidney disease and ESKD (End stage kidney disease). J Paediatr Nurs Sci, 5(3), 145-154. https://doi.org/10.18231/j.ijpns.2022.024
MLA
Mushtaq, Onaisa Aalia, Mushtaq, Bushra, Mir, Javaid Ahmad. "Clinical case report: Chronic kidney disease and ESKD (End stage kidney disease)." J Paediatr Nurs Sci, vol. 5, no. 3, 2022, pp. 145-154. https://doi.org/10.18231/j.ijpns.2022.024
Chicago
Mushtaq, O. A., Mushtaq, B., Mir, J. A.. "Clinical case report: Chronic kidney disease and ESKD (End stage kidney disease)." J Paediatr Nurs Sci 5, no. 3 (2022): 145-154. https://doi.org/10.18231/j.ijpns.2022.024
